Classification of pain
- Spicy.In this case, the pain is severe and even unbearable. It can appear suddenly and disappear suddenly. Often, patients with acute pain can indicate their localization area fairly accurately. Acute pain can radiate, spreading to areas closest to the source of the pathology.
- pain.The pain is not very severe, sometimes uncomfortable, and not exactly localized. The pain may worsen during or after exercise and disappear temporarily.
- Chronic.This category typically includes pain that occurs with varying regularity over six months. Chronic pain is often the most difficult to treat.
Possible sources of pain
- Injuried,
- infectious diseases,
- inflammatory process,
- degenerative tissue changes,
- Pathology of the development of the musculoskeletal system.
Injuried
Hip dislocation in healthy people only occurs after a very strong physical impact, such as a fall from a height or a car accident.
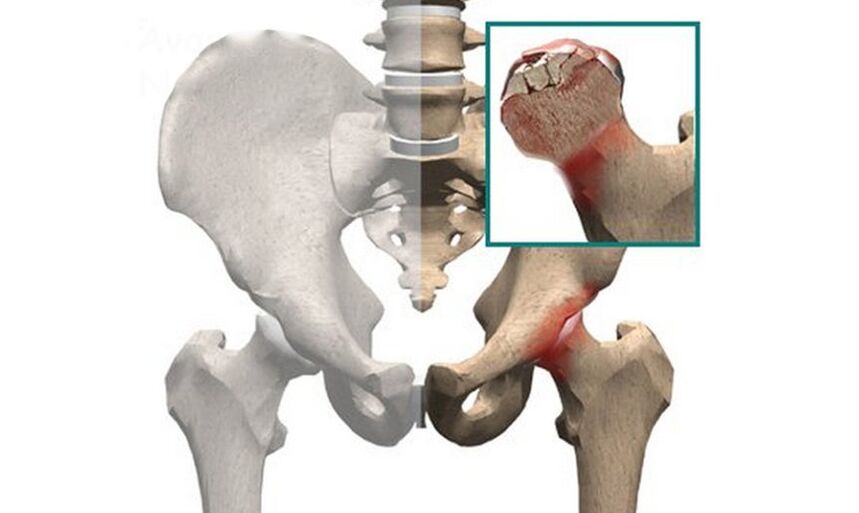
Femoral neck fracture
- Pain in the pelvic area, radiating to the groin and lower back, worsened by tapping the heel;
- shorten the injured leg;
- Limited movement and inability to lean on the injured leg;
- The outwardly rotated position of the limb;
- "Stuck Heel" Syndrome - Inability to lift a straight leg from a lying position.
Fractures of the femoral neck can occur due to impact - in which case the bone fragments become wedged against each other. In this case, the limb's function may be partially or even completely preserved, but when the fragment is crushed, signs of injury are fully apparent. This injury requires immediate intervention, so if you suspect a fracture, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
inflammatory process
- Joint pain, aggravated at night and subsided after activity;
- The formation of subcutaneous compactions, so-called rheumatic nodules, in the affected joint areas;
- Redness, swelling, and localized temperature increase in the affected joint.
Ankylosing spondylitis is an idiopathic disease, which means that in most cases the exact cause of its occurrence cannot be determined. There is a hypothesis that the pathology is genetically determined and that genetic predisposition plays an important role in its development.
degenerative tissue changes
- Pain in the groin, lower back, buttocks, and thighs that worsens with exercise and decreases at rest;
- muscle weakness;
- Intermittent lameness, "duck" gait, and bilateral joint injuries;
- Limb dysfunction, difficulty in abduction, adduction, and rotation.
infectious diseases
With septic arthritis, joint pain is accompanied by redness and swelling of surrounding tissues, as well as general symptoms - fever, malaise, and weakness.
other reasons
- Innervation disorders.Inflammation and compression of nerve roots, especially the sciatic nerve, can lead to pain in the buttocks, inguinal triangle, and buttocks.
- tumor formation, including malignant lesions in joints and surrounding tissues.
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.Chronic poor circulation in the tissues leads to degenerative changes in cartilage and bone tissue and may lead to complete destruction of the bone structure.
- Juvenile epiphyseal dissolution.Chronic hip pain in children and adolescents may be caused by the development of epiphyseolysis, a pathological displacement of the femoral head caused by hormonal disturbances in the body. Boys are more susceptible to this disease, but in rare cases, girls can be diagnosed. Often, the pathology is accompanied by retardation of sexual development and endocrine disorders.
- Weight gain and weight shift, redistribution of load on the musculoskeletal system;
- Natural hormonal changes: Shortly before giving birth, a woman’s body begins producing a hormone that relaxes ligaments;
- The enlarged uterus puts pressure on large blood vessels and nerves, disrupting innervation and blood circulation of the pelvic organs and lower limbs;
- Expectant mothers are deficient in calcium.
If pain during pregnancy is caused by the above factors, then the pain will disappear without a trace a few weeks after birth. If pain persists after one month after the birth of your child, you should consult your doctor.
Alarming symptoms
- Pain in the joints and impaired mobility of the limbs after a fall, blow, bruise or any other injury;
- The tissues around the joints are red and swollen, and the body temperature generally rises to fever levels (above 38°C);
- Problems with bowel movements and urination.
diagnosis
- General, biochemical, serological, immunological blood tests;
- Radiographic examination of the pelvic bones, thighs, and hip joints;
- Ultrasound examination of joint tissue and surrounding tissue;
- MRI and computed tomography to obtain accurate three-dimensional images of the affected area;
- Endoscopy of the joint using a probe inserted into the joint cavity;
- A puncture to study effusion - a pathological accumulation of fluid in the joint capsule;
- Tissue biopsy.
treatment method
Pain syndromes, regardless of their cause, can be relieved by taking analgesics or injectable blockade.
Immobilized
medical treatement
- NSAIDs or corticosteroids to relieve the inflammatory process;
- Chondroprotectants slow degenerative changes in joint tissue;
- Use of antibiotics and antiviral drugs in cases of septic arthritis;
- Muscle relaxants reduce muscle spasms.
physical therapy procedures
- physiotherapy,
- massage,
- magnet therapy,
- balneotherapy,
- Laser Treatment,
- Ultra high frequency heating,
- Leech therapy.
endoprosthesis
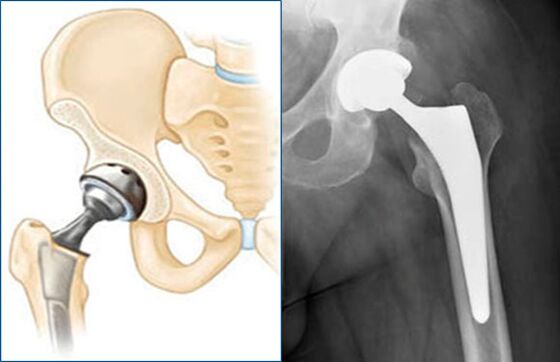
This surgery can shorten the recovery process and allow patients to return to full activity.
Prevent hip pain
- Engage in feasible physical activity regularly to strengthen muscles and ligaments;
- Rich and balanced nutrition;
- Weight control, as overweight and obesity place additional stress on the musculoskeletal system;
- Avoid injury and excessive physical activity;
- Say no to bad habits;
- Prompt and adequate treatment of inflammation and infectious diseases;
- Have regular preventive checkups with your doctor.






















